Smart Assistance for the Blind

How Might We Enable Safe, Confident Navigation for Blind Individuals Through Wearable Tech?
Every day, sighted people move through the world with an invisible safety net, able to see a curb before they trip or dodge an obstacle without a second thought. But for someone who is blind, that safety net does not exist. What we take for granted could mean danger, injury, or worse for them, all because they can’t see what’s coming.

Key Research Topics:
Sketching 1:


Finding First Form




Understanding the Problem Personally:
Before diving into the meat of this project, I wanted to understand what it was like to walk around dealing with blind struggles firsthand. I had the pleasure of connecting with Alaina, Abigail, and Crystal, who are all blind/ visually impaired. As I wanted to gain first-hand experience, they were more than happy to let me spend the day with them walking around their college campus. They led me to their frustration spots where they tend to bang their shins, sternum, or even drop off small ledges (all pictured). From here, I had a clear understanding of specific pain points that are not being addressed and need to be dealt with. I was also able to put 3D printed models of possible forms in their hands so they could feel and give me user feedback on which direction to pursue.
Sketching 2:

Sketching in VR:
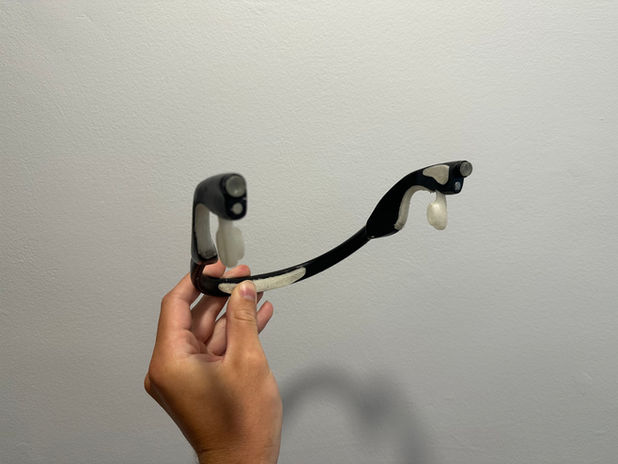
Prototyping:
13+ 3D printed prototypes were made to get to the current form and fit head ergonomics. A Working Prototype has been started but needs to be continued.
Renders and Technologies




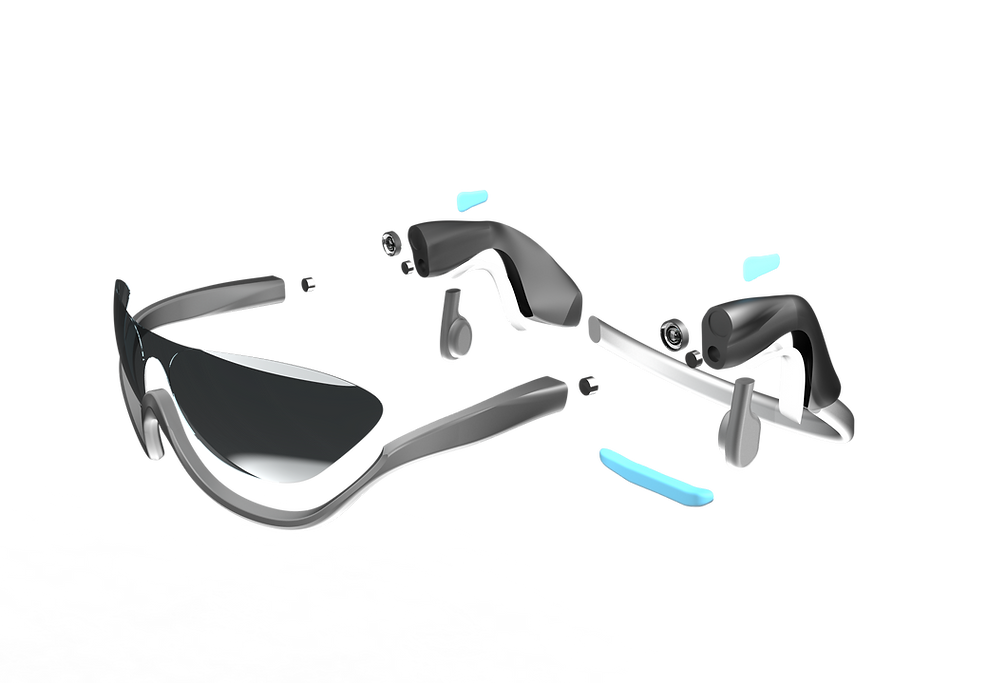
- Modular lens for preferred wear
(magnetic attachment)
Technology in Action

Object Detection - Incoming objects are picked up by 2 depth perception cameras placed on the sides of the head. This is possible through triangulation, as if we know the set distance inbetween the cameras and at what angle each camera sees the object, distance can be calculated.


Notification - Once an object is picked up by cameras, the system can then notify / guide the user out of harms way. the two best way to do this would be through haptic feedback (vibration), or audable feedback (bone conducting headphones

Object Identification - Throughout my research, I learned that not only do the blind bump into many things, but they also want to learn what it is they are bumping into. This could be possible though reverse engineering AI to instead spit out an image of _____ when asked, spit out a description of an object when scanned through the camera.

































